Thyroid Cancer: Symptoms and Diagnosis
Thyroid cancer is the abnormal growth of cells that begins from the thyroid gland at the base of the neck. Neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase, or NTRK gene fusions are key molecular markers in thyroid cancer. The disease has several variations, with each having its degree of aggression. About 33,000 women and 12,000 men are diagnosed with thyroid cancer, and 1100 women and 950 men succumb to the disease annually. Advanced imaging technology allows for early detection and treatment of thyroid cancer. The following are the common symptoms of thyroid cancer:
1. Unexplained hoarseness
According to research, the larynx tissue contains distinct receptors that interact with or bind to thyroid hormones. Given their proximity and connectivity, it is not surprising that thyroid alterations can directly impact an individual’s voice. When thyroid cancer is present, nodules or growths in and around the thyroid gland change their form and put pressure on your larynx and vocal cords. As a result, the voice changes in hoarseness that lasts for weeks, volume fluctuations, and pitch alterations may be a sign of thyroid cancer.
2. Sore throat that doesn’t improve
Sore throats usually go away on their own within a week, making them pretty frequent and generally nothing to be concerned about. However, if the soreness in the throat persists for an extended period, it may be a symptom of thyroid cancer. The persistent sore throat could be a sign of thyroid cancer. Thyroid gland nerve irritations may be the source of the sore throat, and an exceedingly unpleasant cough may occasionally occur causing great discomfort.
3. Difficulty swallowing
Dysphagia is a condition in which a person has to work harder than usual to get food and fluids down their throat. Many people have described the feeling as something stuck in their throat. Swallowing difficulties can be caused by an enlarged thyroid gland’s direct compression of the swallowing organs, thyroid cancer’s invasion, irritation of the nerves, or an unforeseen adverse effect of therapies such as surgery or radiation. A medical evaluation may be required to rule out thyroid cancer if a person has difficulty swallowing or eating solid food that is ordinarily easy to consume.
4. Trouble breathing
Dyspnea (shortness of breath) is a common symptom of thyroid cancer that a generalized respiratory problem may accompany. A physical obstruction causes breathing problems due to an enlarged thyroid gland or nodule pressing up on the esophagus. Changes in spirometry impact the volume of air that flows through the trachea, which frequently results in excessive breathing to compensate for the lack of oxygen. Furthermore, there has been a significant reduction in respiratory muscle strength, which is common in the final stages of the disease. Therefore, people should seek medical attention whenever they notice these symptoms.
5. Swelling in the neck
The primary indication of thyroid cancer is a painless lump or swelling at the front of the neck, directly below Adam’s apple. Some women have Adam’s apples, but they are much smaller and less conspicuous than men’s. The lymph nodes in the neck enlarge and are impacted in the early stages of thyroid cancer. Lymph nodes are small glands part of the lymphatic system, which aid in infection defense. Thyroid nodules or thyroid enlargement could cause sudden shirt tightening without significant weight gain signifying that one may be suffering from thyroid cancer.
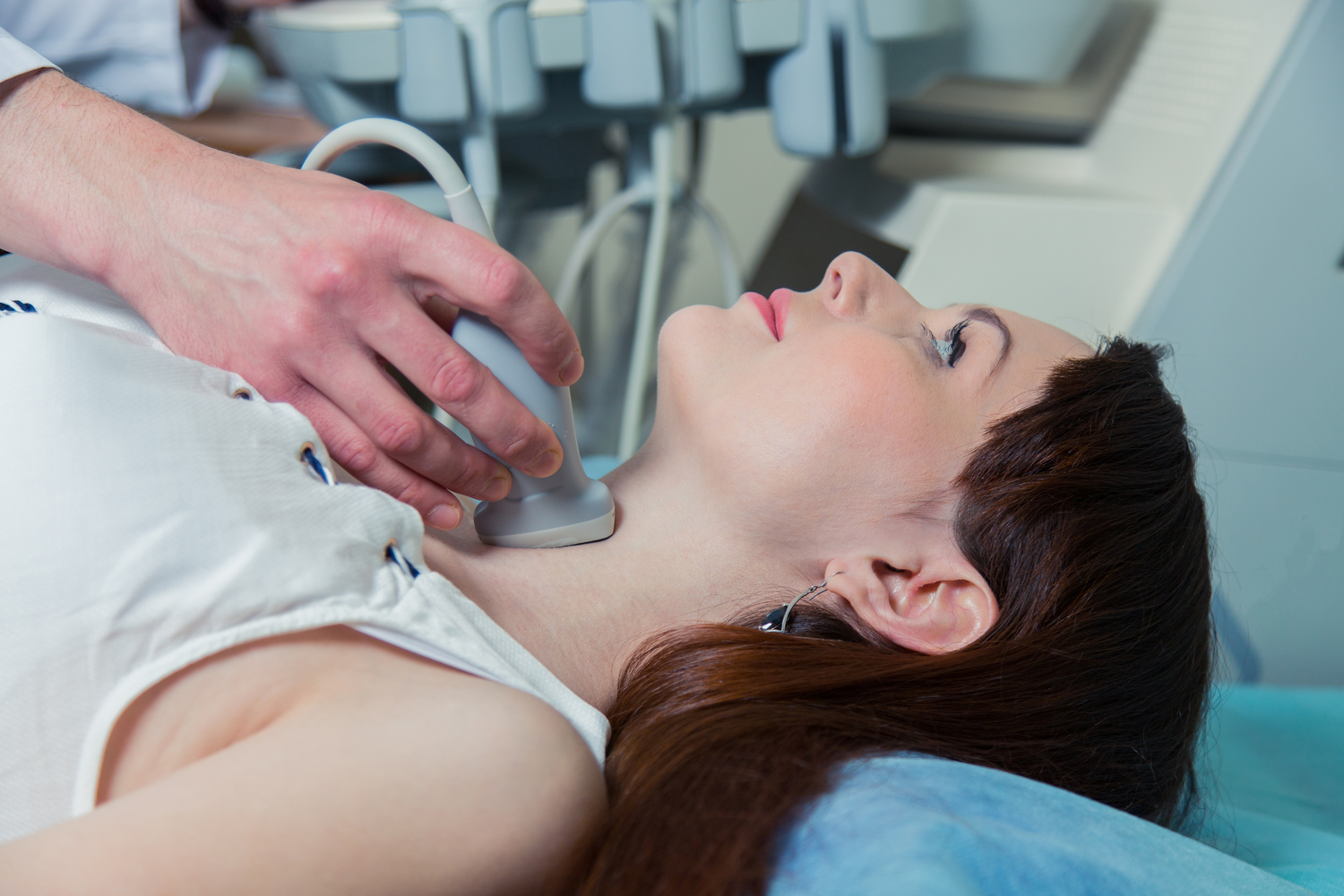
The main way that thyroid cancer is diagnosed is via a FNA (fine needle aspiration) biopsy, in which cells from a nodule or abnormal mass are extracted and examined further in the lab to determine the presence of cancer. If cancer is found, most thyroid tumors are Most cancers are treated with removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) in cases where abnormal cells have not spread outside the thyroid gland. If the cancer has spread, patients are often treated with a combination of surgery, in addition to radioactive iodine therapy for thyroid cancer and targeted oral medications such as GAVRETO (Pralsetinib).